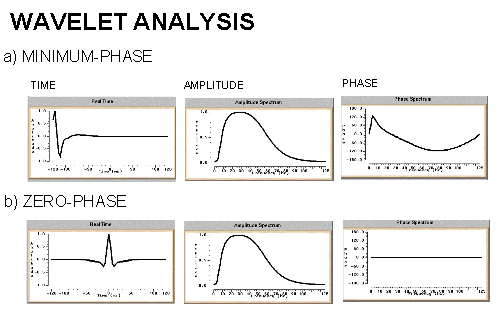
both are wave phases results from the energy souce zero phase wavelet is symmetric on the origin and it is produced from vibrosis
minimum phase is a wave with zero amplitude at the origin it is produced from other sources of energy
for processing all waves must be in minimum phase
The minimum phase wavelet has a short time duration and a concentration of energy at the start of the wavelet. It is zero before time zero (causal). An ideal seismic source would be a spike (maximum amplitude at every frequency), but the best practical one would be minimum phase. It is quite common to convert a given wavelet source wavelet into it's minimum phase equivalent since several processing stages (e.g. predictive deconvolution) work best by assuming that the input data is minimum phase. The maximum phase wavelet is the time reverse of the minimum phase and at every point the phase is greater for the maximum than the minimum. All other causal wavelets are strictly speaking mixed-phase and will be of longer time duration. The convolution of two minimum phase wavelets is minimum phase. The zero-phase wavelet is of shorter duration than the minimum phase equivalent. The wavelet is symmetrical with a maximum at time zero (non-causal). The fact that energy arrives before time zero is not physically realisable but the wavelet is useful for increased resolving power and ease of picking reflection events (peak or trough). The convolution of a zero-phase and minimum phase wavelet is mixed phase (because the phase spectrum of the original minimum phase wavelet is not the unique minimum phase spectrum for the new modified wavelet) and should be avoided
and now the question is what are the types of core analysis?
minimum phase is a wave with zero amplitude at the origin it is produced from other sources of energy
for processing all waves must be in minimum phase
The minimum phase wavelet has a short time duration and a concentration of energy at the start of the wavelet. It is zero before time zero (causal). An ideal seismic source would be a spike (maximum amplitude at every frequency), but the best practical one would be minimum phase. It is quite common to convert a given wavelet source wavelet into it's minimum phase equivalent since several processing stages (e.g. predictive deconvolution) work best by assuming that the input data is minimum phase. The maximum phase wavelet is the time reverse of the minimum phase and at every point the phase is greater for the maximum than the minimum. All other causal wavelets are strictly speaking mixed-phase and will be of longer time duration. The convolution of two minimum phase wavelets is minimum phase. The zero-phase wavelet is of shorter duration than the minimum phase equivalent. The wavelet is symmetrical with a maximum at time zero (non-causal). The fact that energy arrives before time zero is not physically realisable but the wavelet is useful for increased resolving power and ease of picking reflection events (peak or trough). The convolution of a zero-phase and minimum phase wavelet is mixed phase (because the phase spectrum of the original minimum phase wavelet is not the unique minimum phase spectrum for the new modified wavelet) and should be avoided

and now the question is what are the types of core analysis?