+3
moony
salheen
mohammed radwan
7 مشترك
جاوب واسال

mohammed radwan- مراسل المنصورة

 عدد الرسائل : 353
عدد الرسائل : 353
العمر : 36
Localisation : mansoura
Emploi : 3rd geophysics studient
university : mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 28/08/2007
- مساهمة رقم 1
 جاوب واسال
جاوب واسال
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
الفكره دي منقوله من اخوناtarek yehia
انا بس حبيت انقلها عندنا في منتدي الجيوفيزياء
تسال سؤال ، واللي يجاوب علي السؤال صح له حق انه يسال سؤال للي بعده وهكذا
عايزين بس ننشط معلوماتنا في الجيوفيزياء
انا عارف ان الحكايه ممكن تكون صعبه شويه هنا لان عددنا قليل في المنتدي .....لكن ممكن نعمل شغل جامد
شكرا
واحد يحط سؤال بسرعه بقي

salheen- المشرف العام

 عدد الرسائل : 286
عدد الرسائل : 286
العمر : 36
Localisation : nasr city
university : Ain Shams
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/07/2007
- مساهمة رقم 2
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
عرف معامل الانعكاس
مع وضع القانون وخلافه
reflection coefficient

moony- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 77
عدد الرسائل : 77
Localisation : alexandria
Emploi : student
university : alexandria university
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 3
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
reflection coeffecient :it is the ratio between the amlitude of reflected wave to that of incident wave[/size]
[color=darkorchid]for two media sepatated by interface in which the densities are[color=#6600cc]2ρ,1ρ and velocitiesV1and V2 the reflection coeffecient is
[R = (ρ2 V2 - ρ1 V1) / (ρ2 V2 + ρ1 V1
and the question is
what r the types of resolution and how the r improved during processing?
[color=darkorchid]for two media sepatated by interface in which the densities are[color=#6600cc]2ρ,1ρ and velocitiesV1and V2 the reflection coeffecient is
[R = (ρ2 V2 - ρ1 V1) / (ρ2 V2 + ρ1 V1
and the question is
what r the types of resolution and how the r improved during processing?

mohammed radwan- مراسل المنصورة

 عدد الرسائل : 353
عدد الرسائل : 353
العمر : 36
Localisation : mansoura
Emploi : 3rd geophysics studient
university : mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 28/08/2007
- مساهمة رقم 4
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
resolution
depth
ivcrease depth
decrease frequency
decrease resolution
increase velocity
increase wavelength
vertical resolution
governed by wavelength
wavelength=velocity/frequency
so deal with vertical bed thickness
horizontal resolution
three dimension of wave spreading...........etc
measured in terms of fresnel zone
make this for fresnel zone bofore and after migration and know the difference
shoud have frequency less than nyquest
to improve
gathering refracted wave arrivals into common midpoint trace gathers
dsplay data as velocity stacks
put geophones in offset with sources to have the refraction of the structure
there is more tha this but me forget
the question now
what about weathering corrections? how done

moony- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 77
عدد الرسائل : 77
Localisation : alexandria
Emploi : student
university : alexandria university
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 5
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
thanks for answer but i want to add something about resolution improvement
vertical resolution is improved by deconvelution , while horizontal resolution is improved by migration
vertical resolution is improved by deconvelution , while horizontal resolution is improved by migration

uno- مراسل الاسكندرية

 عدد الرسائل : 217
عدد الرسائل : 217
العمر : 36
Localisation : Alexandria
Emploi : geochemistry student
university : Alexandria
تاريخ التسجيل : 15/06/2007
- مساهمة رقم 6
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
Differential weathering is the difference in travel time at opposite ends of split-dip spread for a reflection from a horizon bed.
It is a type of static correction and is induced by low velocity layer such as the weathered layer near the earth's surface.
My question is
what is the difference between convolution and deconvolution?

moony- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 77
عدد الرسائل : 77
Localisation : alexandria
Emploi : student
university : alexandria university
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 7
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
convolution: _kon, v_ loo’ sh_n_ Change in waveshape as
a result of passing through a linear filter.
deconvolution: _de kon vo¯’ lu¯ sh_n_ 1. A process designed
to restore a waveshape to the form it had before it
underwent a linear filtering action _convolution_;
inverse filtering. The objective of deconvolution is to
nullify objectionable effects of an earlier filter action
and thus improve the recognizability and resolution of
reflected events

a result of passing through a linear filter.
deconvolution: _de kon vo¯’ lu¯ sh_n_ 1. A process designed
to restore a waveshape to the form it had before it
underwent a linear filtering action _convolution_;
inverse filtering. The objective of deconvolution is to
nullify objectionable effects of an earlier filter action
and thus improve the recognizability and resolution of
reflected events


uno- مراسل الاسكندرية

 عدد الرسائل : 217
عدد الرسائل : 217
العمر : 36
Localisation : Alexandria
Emploi : geochemistry student
university : Alexandria
تاريخ التسجيل : 15/06/2007
- مساهمة رقم 8
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
thanx ya moony 4 ur clear answer
but
u forgat ask us the Question

takey- جيو صاعد

 عدد الرسائل : 41
عدد الرسائل : 41
العمر : 39
Emploi : Geophysicist
university : Mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 07/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 9
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
ok , I will ask, I know that moony will not remonstrate 
what is the ambiguity??
ana shyef en el maodo3 zareef ya reet nekamlo.....
what is the ambiguity??
ana shyef en el maodo3 zareef ya reet nekamlo.....

CHEETOS- جيو تحت التمرين

 عدد الرسائل : 9
عدد الرسائل : 9
university : ASIC FOR GEOLOGY AND MINING
تاريخ التسجيل : 16/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 10
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
ana mesh fahem elmawdoooo3 mashy ezzay

CHEETOS- جيو تحت التمرين

 عدد الرسائل : 9
عدد الرسائل : 9
university : ASIC FOR GEOLOGY AND MINING
تاريخ التسجيل : 16/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 11
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
what is the meaning of gis&diffrintial gps
7ad yegawep
yallaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaah
7ad yegawep
yallaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaah

mohammed radwan- مراسل المنصورة

 عدد الرسائل : 353
عدد الرسائل : 353
العمر : 36
Localisation : mansoura
Emploi : 3rd geophysics studient
university : mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 28/08/2007
- مساهمة رقم 12
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
بص يا عم شيتوس
الموضوع فكرته
ان فيه سؤال لما تجاوبه صح لك حق انك تسال سؤال
وهكذا
بس
نحاول بس نكمل معلومات لبعض
using some process techniques
or by put reciever on basr station and comparing between locations , the difference is due to he rcording of second the rove reciever
for this comapision need somr info about quality GIS records
data collected using GPS for GIS
this is due to my readings , i donot have yet gis
الموضوع فكرته
ان فيه سؤال لما تجاوبه صح لك حق انك تسال سؤال
وهكذا
بس
نحاول بس نكمل معلومات لبعض
takey question
ambiguity
that thing that cannot be described directly
say this anomaly may be....or it may be.... not have the adaquate answer
non uniqness
can solve proplem by velocity boreholes to study subsurface velocities
also using measurments from several offsets to study velocities chang with depth
this proplems can be solved to acceptable level sometimes
tell me takey alot about meaning of ambiuity in u work
cheetos question
dgps
correction done on data of gps error due to time &increase qualityusing some process techniques
or by put reciever on basr station and comparing between locations , the difference is due to he rcording of second the rove reciever
for this comapision need somr info about quality GIS records
data collected using GPS for GIS
this is due to my readings , i donot have yet gis
my question
there is four methods of resistivity survey design of electrodes
schlumberger
wenner
dipole dipole
pole dipole
tell about
thanks

moony- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 77
عدد الرسائل : 77
Localisation : alexandria
Emploi : student
university : alexandria university
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 13
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
Electrode Arrays
A. Wenner: Alternating +ve and –ve near-surface regions cancel, and main response is from depth, which is fairly uniform laterally. Good for determining depth variations in 1-D Earth.
B. Schlumberger: Equivalent vertical resolution to Wenner (distance between contours), but deep response is concave upwards. More sensitive to lateral variation in Earth.
C.Dipole-Dipole: Poor vertical resolution as contours spaced widely. Lobes from each dipole penetrate deeply indicating good sensitivity to lateral variation at depth

and now the question
what is multiprobe tester (MDT) and its uses?
- An electrode array consists of two electrodes at which DC current flows into and out of the ground plus two electrodes between which the potential difference at the surface is measured .
- The apparent resistivity measured by different arrays is not the same, because the geometric factor K is different.
A. Wenner: Alternating +ve and –ve near-surface regions cancel, and main response is from depth, which is fairly uniform laterally. Good for determining depth variations in 1-D Earth.
B. Schlumberger: Equivalent vertical resolution to Wenner (distance between contours), but deep response is concave upwards. More sensitive to lateral variation in Earth.
C.Dipole-Dipole: Poor vertical resolution as contours spaced widely. Lobes from each dipole penetrate deeply indicating good sensitivity to lateral variation at depth

and now the question
what is multiprobe tester (MDT) and its uses?

takey- جيو صاعد

 عدد الرسائل : 41
عدد الرسائل : 41
العمر : 39
Emploi : Geophysicist
university : Mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 07/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 14
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
MDT "Modular Formation Dynamics Tester", the MDT tool offers multiple sampling during a single wireline run and rapid pressure measurement using a new generation
quartz gauge that stabilized quickly to accurately measure the formation
pressure.
Improved electrohydraulic control more easily minimizes the drawdown pressure drop,
enhancing delicate sampling operations. A variable drawdown volume improves
permeability measurement, especially in tight formations.
The MDT system comprises a number of modules such as Electrical module, hydraulic
power module, single-probe module, Sample chamber module, multisample module, pumpout
module, flow control module, multiprobe module and Dual-packer module.
I hope this is the answer.
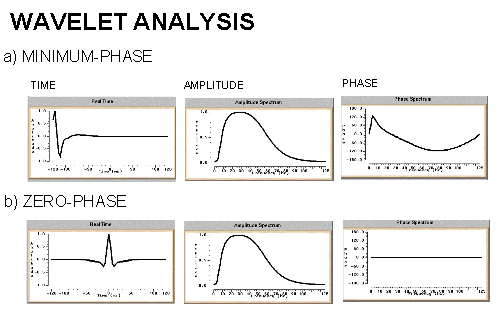
What is the Zero and minimum phase ?
quartz gauge that stabilized quickly to accurately measure the formation
pressure.
Improved electrohydraulic control more easily minimizes the drawdown pressure drop,
enhancing delicate sampling operations. A variable drawdown volume improves
permeability measurement, especially in tight formations.
The MDT system comprises a number of modules such as Electrical module, hydraulic
power module, single-probe module, Sample chamber module, multisample module, pumpout
module, flow control module, multiprobe module and Dual-packer module.
I hope this is the answer.
What is the Zero and minimum phase ?

mohammed radwan- مراسل المنصورة

 عدد الرسائل : 353
عدد الرسائل : 353
العمر : 36
Localisation : mansoura
Emploi : 3rd geophysics studient
university : mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 28/08/2007
- مساهمة رقم 15
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
very diffucult question takey
any one know should tell
i think takey will answer it finally

moony- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 77
عدد الرسائل : 77
Localisation : alexandria
Emploi : student
university : alexandria university
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 16
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
both are wave phases results from the energy souce zero phase wavelet is symmetric on the origin and it is produced from vibrosis
minimum phase is a wave with zero amplitude at the origin it is produced from other sources of energy
for processing all waves must be in minimum phase
The minimum phase wavelet has a short time duration and a concentration of energy at the start of the wavelet. It is zero before time zero (causal). An ideal seismic source would be a spike (maximum amplitude at every frequency), but the best practical one would be minimum phase. It is quite common to convert a given wavelet source wavelet into it's minimum phase equivalent since several processing stages (e.g. predictive deconvolution) work best by assuming that the input data is minimum phase. The maximum phase wavelet is the time reverse of the minimum phase and at every point the phase is greater for the maximum than the minimum. All other causal wavelets are strictly speaking mixed-phase and will be of longer time duration. The convolution of two minimum phase wavelets is minimum phase. The zero-phase wavelet is of shorter duration than the minimum phase equivalent. The wavelet is symmetrical with a maximum at time zero (non-causal). The fact that energy arrives before time zero is not physically realisable but the wavelet is useful for increased resolving power and ease of picking reflection events (peak or trough). The convolution of a zero-phase and minimum phase wavelet is mixed phase (because the phase spectrum of the original minimum phase wavelet is not the unique minimum phase spectrum for the new modified wavelet) and should be avoided
and now the question is what are the types of core analysis?
minimum phase is a wave with zero amplitude at the origin it is produced from other sources of energy
for processing all waves must be in minimum phase
The minimum phase wavelet has a short time duration and a concentration of energy at the start of the wavelet. It is zero before time zero (causal). An ideal seismic source would be a spike (maximum amplitude at every frequency), but the best practical one would be minimum phase. It is quite common to convert a given wavelet source wavelet into it's minimum phase equivalent since several processing stages (e.g. predictive deconvolution) work best by assuming that the input data is minimum phase. The maximum phase wavelet is the time reverse of the minimum phase and at every point the phase is greater for the maximum than the minimum. All other causal wavelets are strictly speaking mixed-phase and will be of longer time duration. The convolution of two minimum phase wavelets is minimum phase. The zero-phase wavelet is of shorter duration than the minimum phase equivalent. The wavelet is symmetrical with a maximum at time zero (non-causal). The fact that energy arrives before time zero is not physically realisable but the wavelet is useful for increased resolving power and ease of picking reflection events (peak or trough). The convolution of a zero-phase and minimum phase wavelet is mixed phase (because the phase spectrum of the original minimum phase wavelet is not the unique minimum phase spectrum for the new modified wavelet) and should be avoided

and now the question is what are the types of core analysis?

takey- جيو صاعد

 عدد الرسائل : 41
عدد الرسائل : 41
العمر : 39
Emploi : Geophysicist
university : Mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 07/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 17
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
Excellent answer moony



takey- جيو صاعد

 عدد الرسائل : 41
عدد الرسائل : 41
العمر : 39
Emploi : Geophysicist
university : Mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 07/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 18
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
The Major Types of Core Analysis
Full-Diameter Analysis
Routine Analysis
Pressure Core Analysis
Sponge Core Analysis
Sidewall Core Analysis
1. Plug (Conventional) Analysis
a. Consolidated Formations
This technique is normally
restricted to homogeneous formations that can be characterized with plug-size
samples. Typical plug size is 1 inch (2.5 m) in diameter, and 1 inch (2.5 cm)
long.
b. Unconsolidated Formations
Unconsolidated
sand recovered within a rubber sleeve core barrel, a plastic inner barrel
liner, or a fiberglass barrel is often stabilized by freezing prior to
sampling. Frozen interstitial water present at the grain contacts immobilizes
the rock particles. Plugs are drilled using liquid nitrogen as the bit
lubricant.
2. Full Diameter Analysis
a. Routine Analysis
Full
diameter analysis was introduced to allow testing of rocks with complex
lithology, such as heterogeneous carbonates and fissured, vugular formations
unsuitable for plug analysis.
b. Pressure Core Analysis
The analysis of full diameter
pressure cores follows, in a modified form, the procedures normally employed in
more routine analysis. Full diameter samples are cut in the form of a right
cylinder and then placed in specialized, airtight containers where they thaw,
so that fluids expulsed from the core can be collected and measured.
c. Sponge Core Analysis
Full diameter analysis of
samples recovered within the sponge barrel proceeds along the usual lines once
the core has been removed from the barrel. The sponge itself is cut from the
core barrel and the fluids it contains are extracted using a vacuum retort
technique. Both oil and water volumes within the sponge are measured.
3. Sidewall Core Analysis
Sidewall samples are used extensively
in softer sand areas. (Note, however, that a sidewall-drilled plug from a new
sidewall coring device can be used for harder formations and can be analyzed in
the same manner as a standard plug-sized core.) Percussion sidewalls are often
smaller and demand additional attention.
Now Easy Question
What is the Ground roll??
- Plug (Conventional) Analysis
- Consolidated Formations
- UnconsolidatedFormations
1. Plug (Conventional) Analysis
a. Consolidated Formations
This technique is normally
restricted to homogeneous formations that can be characterized with plug-size
samples. Typical plug size is 1 inch (2.5 m) in diameter, and 1 inch (2.5 cm)
long.
b. Unconsolidated Formations
Unconsolidated
sand recovered within a rubber sleeve core barrel, a plastic inner barrel
liner, or a fiberglass barrel is often stabilized by freezing prior to
sampling. Frozen interstitial water present at the grain contacts immobilizes
the rock particles. Plugs are drilled using liquid nitrogen as the bit
lubricant.
2. Full Diameter Analysis
a. Routine Analysis
Full
diameter analysis was introduced to allow testing of rocks with complex
lithology, such as heterogeneous carbonates and fissured, vugular formations
unsuitable for plug analysis.
b. Pressure Core Analysis
The analysis of full diameter
pressure cores follows, in a modified form, the procedures normally employed in
more routine analysis. Full diameter samples are cut in the form of a right
cylinder and then placed in specialized, airtight containers where they thaw,
so that fluids expulsed from the core can be collected and measured.
c. Sponge Core Analysis
Full diameter analysis of
samples recovered within the sponge barrel proceeds along the usual lines once
the core has been removed from the barrel. The sponge itself is cut from the
core barrel and the fluids it contains are extracted using a vacuum retort
technique. Both oil and water volumes within the sponge are measured.
3. Sidewall Core Analysis
Sidewall samples are used extensively
in softer sand areas. (Note, however, that a sidewall-drilled plug from a new
sidewall coring device can be used for harder formations and can be analyzed in
the same manner as a standard plug-sized core.) Percussion sidewalls are often
smaller and demand additional attention.
Now Easy Question
What is the Ground roll??

hosny hassan- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 68
عدد الرسائل : 68
العمر : 37
Localisation : alexandia, egypt
university : geophysics departement
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 19
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
ØSurface waves (often called ground roll) are usually present on reflection records
ØFor the most part, these are Rayleigh waves with velocities ranging from 100 to 1000 m/s or so.
ØGround roll frequencies usually are lower than those of reflection and refractions, often with the energy concentrated below 15 Hz.
ØGround roll alignments are straight, just as refractions are, but represent lower velocities.
ØGround roll energy generally is high enough even in the reflection band to override all but the strongest reflections.
ØOccasionally where ground roll is exceptionally strong, in line offsets are used so that desired reflections can be recorded before the surface waves reach the spread.


hosny hassan- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 68
عدد الرسائل : 68
العمر : 37
Localisation : alexandia, egypt
university : geophysics departement
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 20
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
i hope this answer will be sufficient
my next question
what is Dip moveout processing?
thank u takey about this answer

takey- جيو صاعد

 عدد الرسائل : 41
عدد الرسائل : 41
العمر : 39
Emploi : Geophysicist
university : Mansoura
تاريخ التسجيل : 07/10/2007
- مساهمة رقم 21
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
A
traveltime curve resulting from a dipping reflector has two velocity
components. The first component is the normal moveout component, which is a
factor of the geometry of the seismic array and the increasing distance from
the zero offset location to the far receivers. The second component is caused
by the presence of structural dip.
This
second component is reflected in the asymmetry of the travel paths on either
side of the zero offset location. Travel paths on the updip side have shorter
raypaths and, therefore, faster traveltimes than those on the downdip side.
This phenomenon is most apparent with shot gather data, but it also occurs on a
smaller scale with CMP gather data.
The first velocity component is taken into account by
applying a normal move-out (NMO) correction. The second is handled by
applying a dip moveout (DMO) correction.
While NMO corrects for the time
delay on an offset trace by moving the amplitudes to earlier times on the trace,
DMO moves the data up-dip to the correct position where a zero-offset trace
would record a dipping reflector (Figure 1). Migration then moves the energy to
the correct horizontal and vertical subsurface location.
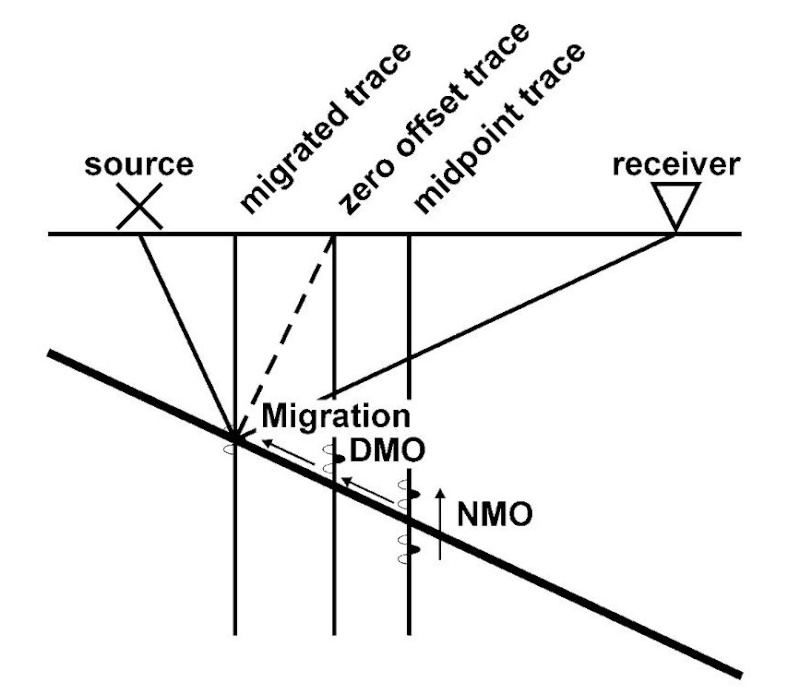
Fig. 1. Data movement during NMO, DMO, and
migration (after Sheriff, 1991).

Figure 2 and Figure 3 are
an example of data in a highly faulted area. In this case, DMO improves the
data quality. In Figure 2 , the arrows point to a reflector that appears to be
fairly continuous. But in Figure 3 , we can see that the reflector is faulted
and that DMO has improved the overall fault definition in this area
Finally, we can say that the DMO “Dip MoveOut”
is A geophysical process which corrects for differences in arrival times at
different geophone offset positions caused by the dip of a reflector.
Now what do u know about (OBC) ocean-bottom cable?

hosny hassan- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 68
عدد الرسائل : 68
العمر : 37
Localisation : alexandia, egypt
university : geophysics departement
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 22
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
weeeeeeeehaa very nice takey
thank u very much
really really really thanks
the answer of your question is ready

hosny hassan- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 68
عدد الرسائل : 68
العمر : 37
Localisation : alexandia, egypt
university : geophysics departement
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 23
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
Ocean Bottom Seismograph (OBS)
In the 1990s, the introduction of Ocean Bottom Cable (OBC), where the seismic cables are laid down on the sea bottom
A particular kind of OBC includes two seismic sensors, one hydrophone and one multicomponent receiver. The hydrophone provides pressure measurements while the multicomponent receiver, which consists of three geophones oriented in directions perpendicular to each other, measures the components of the elastic wavefield.
ØThis particular seismic acquisition method, known as Ocean Bottom Seismograph (OBS), yields satisfactory data quality for S-wave energy in a marine environment.
ØMulticomponent seismic surveys record both P-waves and shear, or S-waves; this is achieved by recording all components of the returning wavefield.
ØEach sensor within a multicomponent recording cable comprises three orthogonally oriented geophones for land acquisition, plus a hydrophone for marine acquisition (hence four-component or 4C).
ØP-waves are detected primarily by the Z-component geophone and the hydrophone, while S-waves are detected primarily by the X- and Y-component geophones.
ØThe 3C data can then be used to “create” the shear wave mode, called a C-wave, by converting the S-wave signal using a P-to-S mode conversion algorithm technique.
A particular kind of OBC includes two seismic sensors, one hydrophone and one multicomponent receiver. The hydrophone provides pressure measurements while the multicomponent receiver, which consists of three geophones oriented in directions perpendicular to each other, measures the components of the elastic wavefield.
ØThis particular seismic acquisition method, known as Ocean Bottom Seismograph (OBS), yields satisfactory data quality for S-wave energy in a marine environment.
ØMulticomponent seismic surveys record both P-waves and shear, or S-waves; this is achieved by recording all components of the returning wavefield.
ØEach sensor within a multicomponent recording cable comprises three orthogonally oriented geophones for land acquisition, plus a hydrophone for marine acquisition (hence four-component or 4C).
ØP-waves are detected primarily by the Z-component geophone and the hydrophone, while S-waves are detected primarily by the X- and Y-component geophones.
ØThe 3C data can then be used to “create” the shear wave mode, called a C-wave, by converting the S-wave signal using a P-to-S mode conversion algorithm technique.
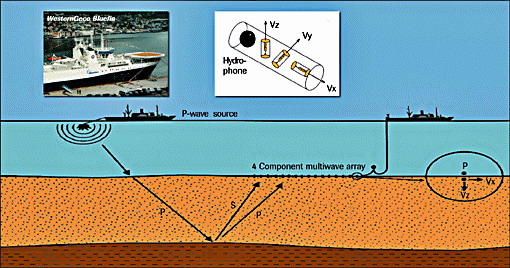

4-C sensor
ØBecause of the nature of the OBS data acquisition, combining the vertical component (Z-component) of the vector wavefield and the pressure component (hydrophone), a process known as PZ summation, produces PZ seismic sections, which are ideally free of water-bottom multiples
ØBecause of the nature of the OBS data acquisition, combining the vertical component (Z-component) of the vector wavefield and the pressure component (hydrophone), a process known as PZ summation, produces PZ seismic sections, which are ideally free of water-bottom multiples


ØThe PS sections of the OBS seismic dataset have proved to be useful in several areas, as for example, the identification of gas seepages, P-wave reflections are disturbed by the presence of gas in the subsurface, however, S-waves help to clarify the subsurface image since they are not affected by the presence of gas.


عدل سابقا من قبل في 2007-12-02, 7:29 am عدل 1 مرات

hosny hassan- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 68
عدد الرسائل : 68
العمر : 37
Localisation : alexandia, egypt
university : geophysics departement
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 24
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
i hope this will help you
i find it great to answer many questions to get more information
this is really good partition in the forum
thanks takey about the question

hosny hassan- جيو محترف

 عدد الرسائل : 68
عدد الرسائل : 68
العمر : 37
Localisation : alexandia, egypt
university : geophysics departement
تاريخ التسجيل : 12/09/2007
- مساهمة رقم 25
 رد: جاوب واسال
رد: جاوب واسال
now my question is
what is the concept of seismic stratigraphy and its applications in determining the real lithology ?


